Translate this page into:
Anterior soft tissue retraction during arthroscopy of the ankle
*Corresponding author: Srinivas B. S. Kambhampati, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sri Dhaatri Orthopaedic Maternity and Gynaecology Center, Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh, India. kbssrinivas@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Kambhampati SB, Chinta S, Chodavarapu M. Anterior soft tissue retraction during arthroscopy of the ankle. J Arthrosc Surg Sports Med. 2024;5:47-50. doi: 10.25259/JASSM_6_2024
Abstract
Ankle arthroscopy has been increasingly employed in recent times due to a wide variety of ankle pathologies and advances in indications and technology. We have described a technique of retraction of the anterior soft tissue structures that can be used during ankle arthroscopy that is easy, does not require special instruments, is quick to apply, and gains valuable tourniquet time by reducing interruptions caused by tissue interference and increasing the visual field.
Keywords
Ankle arthroscopy
Anterior portals
Ethibond
Increased visual field
INTRODUCTION
Arthroscopy of the ankle is on the rise, with increasing indications and improving technology for the procedure. It is important to visualize the structures during an arthroscopy to identify pathologies and implement therapeutic methods. The ankle is a superficial joint with important neurovascular structures lying anteriorly. It is also important to protect these structures during partial excision of the anterior fat pad and synovium during arthroscopy of the ankle. A technique has been described recently for retraction of anterior structures during dry arthroscopy of the ankle.[1] Another technique has been described for the retraction of the infrapatellar fat pad during arthroscopy of the knee.[2] We combine the principles of these two techniques and describe a technique to retract the anterior structures of the ankle during ankle arthroscopy. This has not been reported before, to our knowledge.
TECHNIQUE
Standard anterior portals of the anteromedial (AM) and anterolateral (AL) are placed during arthroscopy of the ankle with or without distraction. Our technique is described without distraction. The AM portal is used for visualizing the scope, and the AL portal is used for instrumentation and probing. It is important to visualize the probe coming from the AL portal to perform this technique. The scope is placed in the direction of the AL portal, and the probe is removed. A knot pusher is loaded with a size 2 Ethibond as a loop, as shown in Figure 1, and it is introduced through the AL portal into the ankle until it is visualized by the scope. The knot pusher with the suture at the head is advanced close to the far end of the scope until it touches the scope. The scope is then unlocked from the cannula and withdrawn partially, which creates space distally in the cannula to advance the knot pusher with its suture. Once the knot pusher is securely engaged in the cannula, the scope is fully withdrawn out of the cannula, and the knot pusher is advanced to the extent that it comes out of the AM portal comfortably inside the cannula. The cannula is then removed, leaving the knot pusher and the suture coming out of the AM portal. The suture is held at the loop, and the knot pusher is withdrawn fully out of the AL portal, leaving just the doubled suture coming out from both portals with a portion inside the joint bridging both portals. Pulling the suture anteriorly increases the space anteriorly [Figure 2] to work during arthroscopy of the ankle. The suture is visualized as a reflection on the shaver blade in Figure 3. This can guide the shaver in avoiding the suture while shaving the ankle. An assistant may be given the suture for retracting [Figure 4] while the surgeon performs the rest of the procedure.
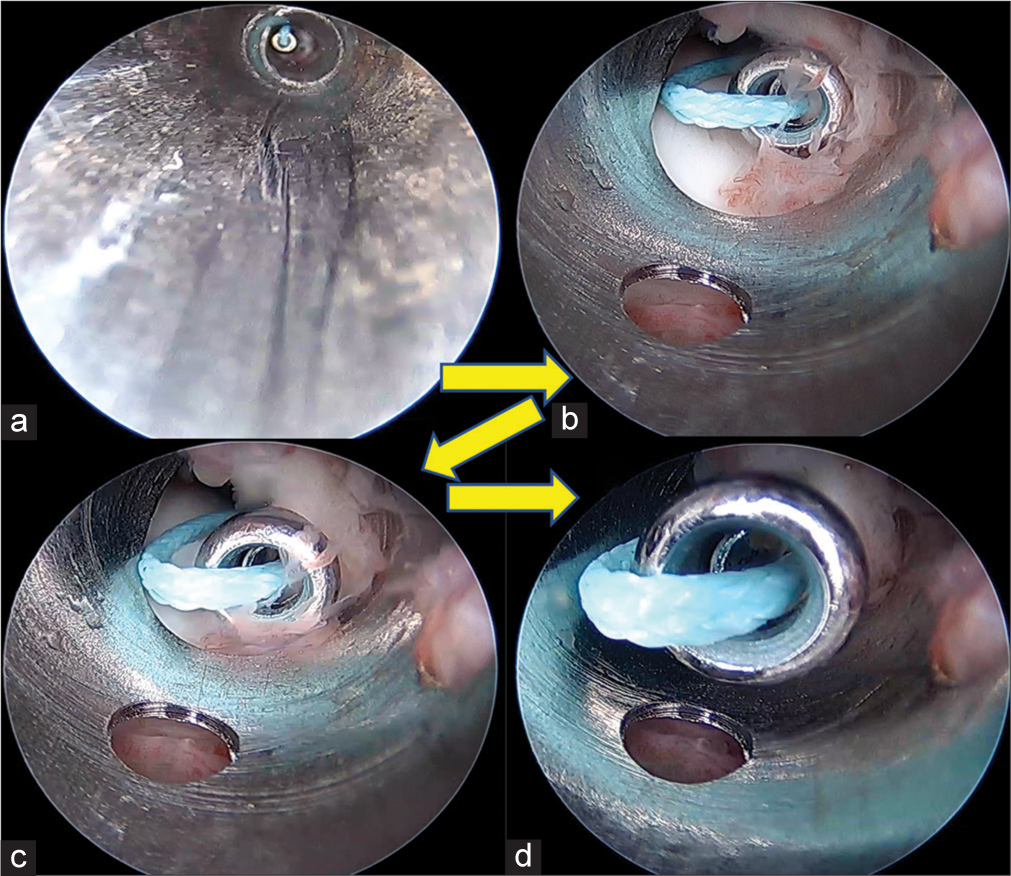
- (a-d) Sequence of inserting suture into the cannula of the scope (arrows point to the progress of events).
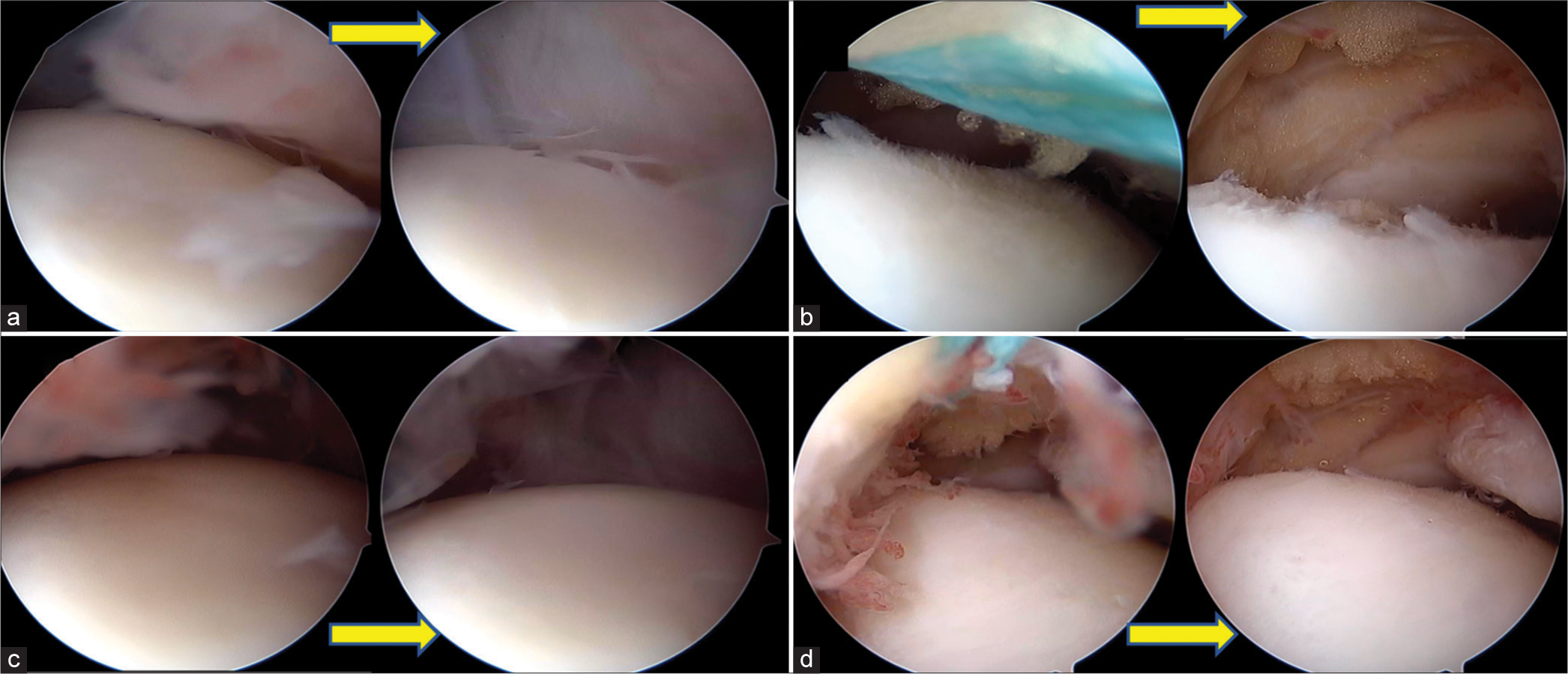
- Each pair of images (a-d) with arrows depicting before and (arrow pointing to after traction image) after traction with the suture. It can be seen that the view of the anterior aspect of the ankle significantly improves after traction in each instance.
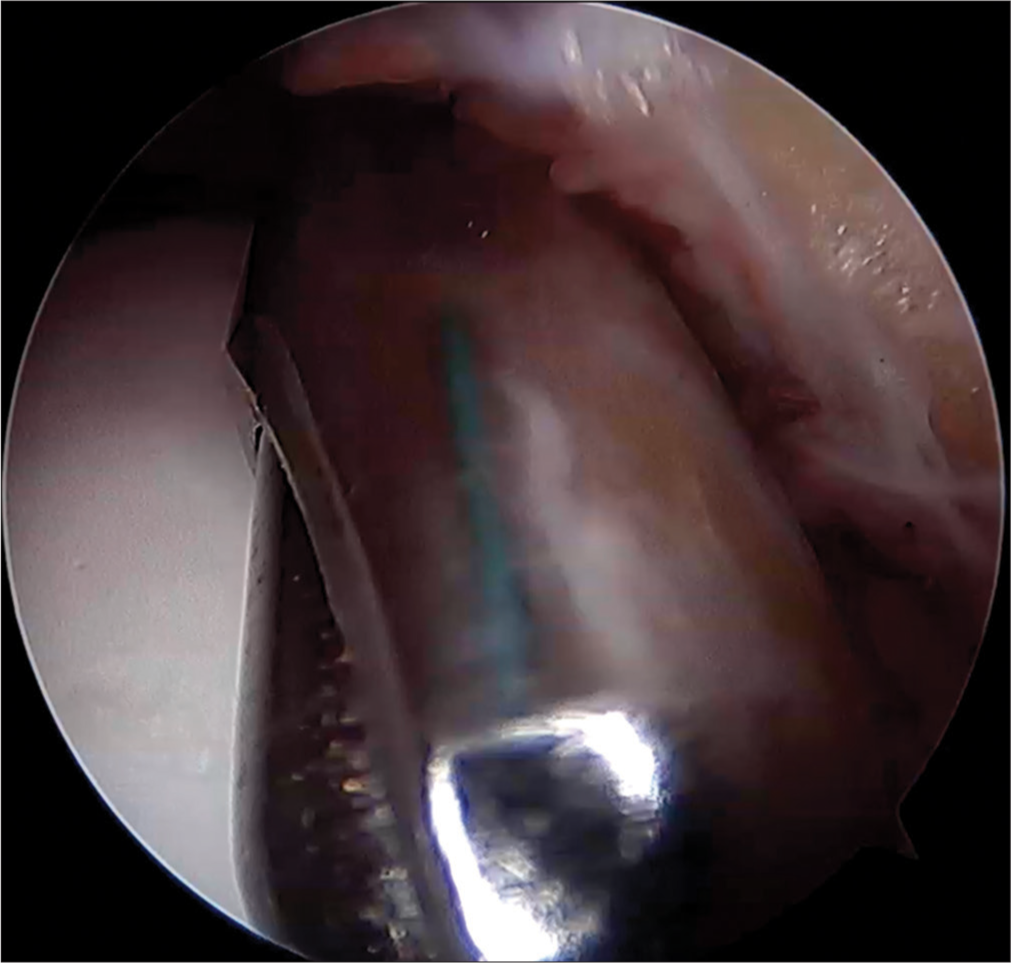
- Reflection of the Ethibond suture seen on the shaver to avoid inadvertently cutting off and marking the position of the capsule.
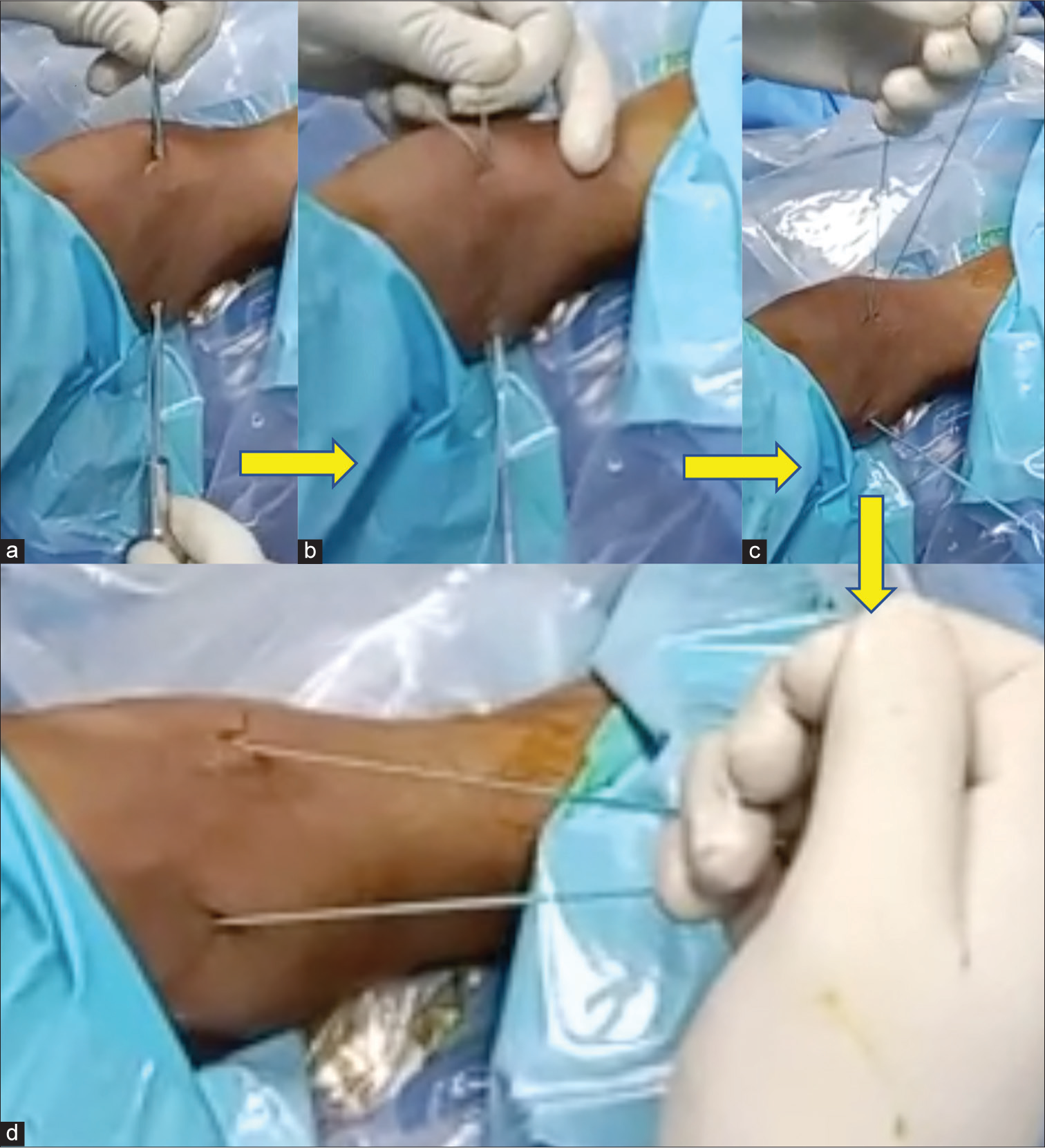
- Steps in placing the retractor. (a) Suture coming out of both portals. (b) Retaining loop on one side pulling out knot pusher, (c) After removal of knot pusher, (d) Final position, ready for retraction. The yellow arrows indicate progression of steps in passing the traction suture.
DISCUSSION
We describe one way to retract the anterior structures during arthroscopy of the ankle. Although the irrigation fluid distends the ankle joint, it may not be adequate in some cases, and placing a retractor improves visualizing the ankle. The space gained by retraction is shown in Figure 2. Although retraction has been employed in the past during ankle arthroscopy, it was for dry arthroscopy, and the authors employed a custom-made implement for the purpose during that procedure. Our technique does not require a custom-made retractor. A size 2 Ethibond suture is adequate and is available in most operation theaters. Even if this is not available, any thick suture may be used for the same purpose, including a size 0 or 1 suture of any material. Our preference is Ethibond due to its color and toughness so that it does not cut easily or accidentally during shaving [Figure 3]. The green color of Ethibond would also mark the position of the capsule while shaving and protect the structures anteriorly during shaving.
Sadlik et al. used a spinal needle to feed the suture.[1] The disadvantage of this technique is that the sharp needle, on occasion, could create a track that is not intended and could make passing sutures difficult. The needle may also injure structures if the track changes. A knot pusher is blunt, easy to pass into the joint through the portals, and does not injure any structure during passing. Due to the diameter of the head, side-tracking into other tissue planes is not easy with the knot pusher.
Frequently, the instruments and scope during reintroduction into a portal may be misdirected away from the joint into the superficial soft tissues while doing a regular ankle arthroscopy. Another advantage of using the retractor is that it maintains the portal patent and serves as a guide for placing the scope or instruments into either portal easily for multiple passes, thus saving time. Furthermore, the space gained with retraction will be more with the ankle in dorsiflexion rather than in plantar flexion. If the space is limited, the scope may need to be placed close to the structure being visualized. After traction is applied, the visual field increases [Figure 2], allowing the drawing back of the scope and increasing the clarity of view and the visual field. The advantages of this technique are that it is easy, does not require special instruments, is quick to apply, and saves valuable tourniquet time by reducing interruptions caused by tissue interference and increasing the visual field. Although not demonstrated here, it may also be employed during dry scopy.
It is important to avoid shaving close to the suture intraarticularly; otherwise, the suture may be cut, and the benefit of retraction may be lost. One disadvantage of this technique is that since it keeps the portal patent, fluid tends to leak through the portals, but the extent is not great, as this happens even when the instrumentation is placed in the portals. Aggressive retraction should be avoided to prevent stretch injuries to the structures being retracted. Further studies may be required to study the complications of ankle arthroscopy for different procedures.
CONCLUSION
Suture retraction is a very simple and useful technique in ankle arthroscopy and may be employed easily when required using the technique we have described.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patient identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Conflicts of interest
Dr. Srinivas B. S. Kambhampati is on the editorial board of the Journal.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Dry arthroscopy with a retraction system for matrix-aided cartilage repair of osteochondral lesions of the talus. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36:339-43.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retraction of infrapatellar fat pad during arthroscopy of the knee. J Arthorsc Surg Sport Med. 2021;2:81-3.
- [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]







